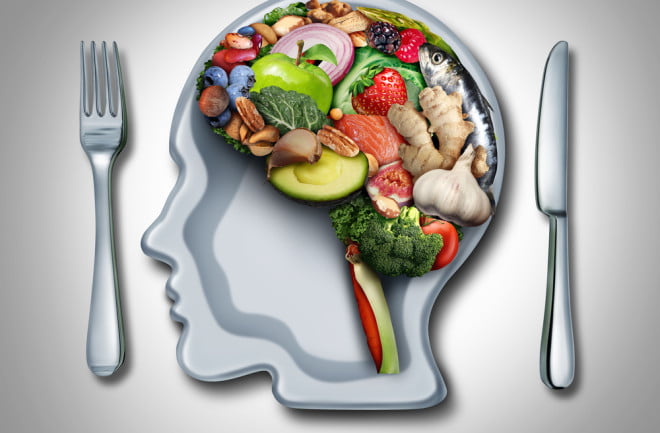
Food can profoundly affect your brain and internal health, just like drugs prescribed by a fraudster. Your gut and brain are constantly communicating with each other. A case of confusion not understanding why I was healing while talking about his stomach. It doesn’t seem to apply to him. She said, “After all, they weren’t together. “Although your brain and gut are located in different corridors, they are still physically connected. The vagus nerve is also known as the ‘gypsy’. It originates in the brain stem and travels to the intestines. Filagra Gel Shots and Isotretinoin 40 Mg Connecting the heart to the central nervous system the vague whim, or “Gypsy whim,” originates in the brain stem and travels to the intestines. It connects the central nervous system with the heart. Whim vagus is important for digestion because it penetrates the intestinal wall. But its main function is that it ensures that stubborn signals and chemicals can travel between the gut and the brain and carry important information.
The love between the gut and the brain
Chemicals are the basis of all bodily communication. In the brain, these chemicals arise from the main corridors of your nervous system (with the help of the endocrine system), the central nervous system, which includes the brain and spinal cord; autonomic nervous system (ans), including the sympathetic and parasympathetic systems; and the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (hpa) axis, which includes the hypothalamus, pituitary, and adrenal glands. The central nervous system produces chemicals similar to serotonin and dopamine.
These chemicals are essential for recycling, emotion, and mood regulation studies. Serotonin is a chemical deficient in the intelligence of people with depression or anxiety. It plays an important role in regulating the gut-brain connection. Serotonin, a brain chemical much talked about because it affects mood and emotions, has more than 90 serotonin receptors in the gut. All of these brain chemicals work together to ensure that the brain and intestines function smoothly in a healthy person. As with all complex systems, effects can always go wrong. The gut-brain connection is disrupted when chemical situations are too high or too low. The stories of important chemicals are unbalanced. The mood is disturbed. Disturbed attention. Exemptions are affected. The intestinal barrier to cover the brain is damaged. Chemicals and metabolites that are intended to stay outside the brain can reach the brain causing destruction.
Food that can affect your brain is just as important as drugs.
Chaos. This chemical can lead to mental illnesses, from depression to anxiety and loss of sex drive. It can also lead to more serious conditions like schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. You might think we need a sophisticated array of drugs to correct this chemical imbalance and restore order to the brain and body. You will be right to some extent! The maturation of drugs used to treat medical conditions alters these chemicals to restore the brain to a healthier state. For example, difficult serotonin reuptake barriers (SSRIs) stimulate serotonin situations to combat depression. The most advanced internal medicine can save lives and its importance in treatment must not be underestimated. However, what is often overlooked in internal wellness conversations is the simple fact that food can affect your mind as deeply as drugs.
Gut microbiota.
A large set of microorganisms in the gut are responsible for the love between the gut and the brain. Humans and organisms have gut microbiota, a type of relationship in which both parts depend on each other for survival. In exchange for providing bacteria with a home to grow and live in, our intestines perform important tasks that we cannot do on our own. The microbiome is made up of many types of bacteria. In the gut, there are more species than anywhere else. A person’s microbiome can contain more than 1,000 different species of bacteria. However, these mature bacteria belong to only two groups firmicutes and Bacteroides.
These two groups represent 75 of all microbiomes. Fairly new in drugs to honor bacteria that can affect brain function. Over time, wisdom has shown that gut bacteria influence internal function. Functional intestinal conditions, similar to dyspepsia or dyspepsia, can lead to mood swings due to altered bacterial populations. Probiotics may help reduce anxiety and depression. However, they also start to pass on the symptoms of schizophrenia, if you put the gut bacteria of people with schizophrenia into the stomachs of mice. Normal gut bacteria are essential for the production of neurotransmitters such as dopamine, glutamate, and gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), which are essential for mood regulation, memory, and attention. The right balance of bacteria in your gut is essential for the brain to produce the chemicals it needs to stay stable and healthy. Your brain needs to be strong and healthy for your gut to maintain the right balance of bacteria. This cyclical relationship can break down and cause problems for the brain and heart. A healthy gut microbiome can lead to a healthy brain and vice versa.